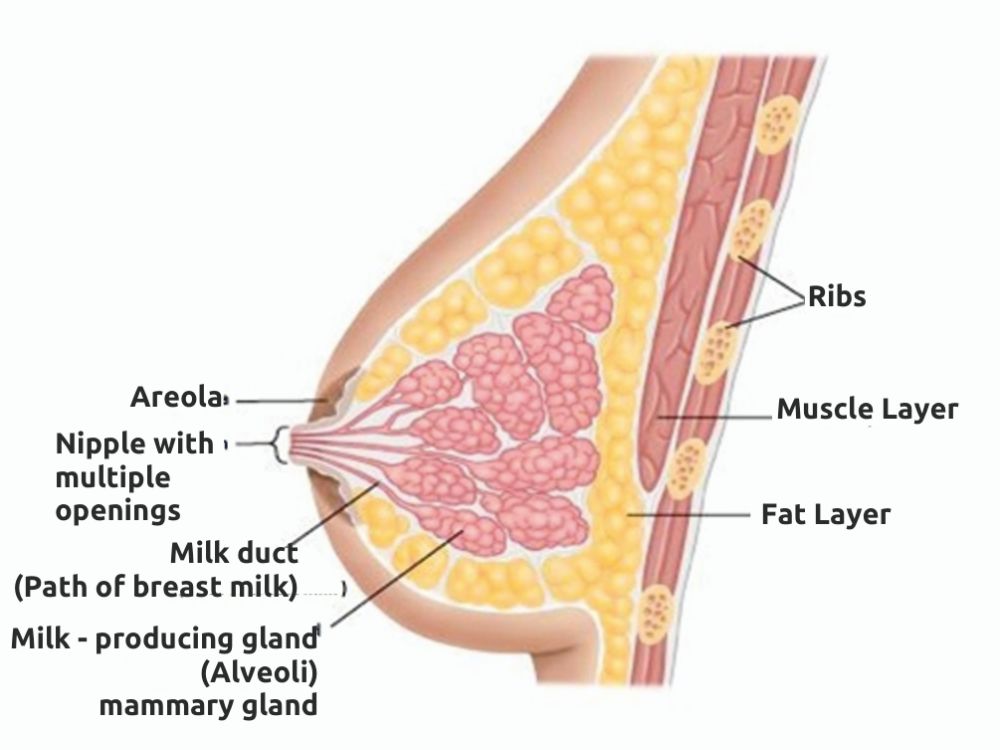
Anatomy of Breast
Breastfeeding
Following image showing some position for breast feeding your baby.
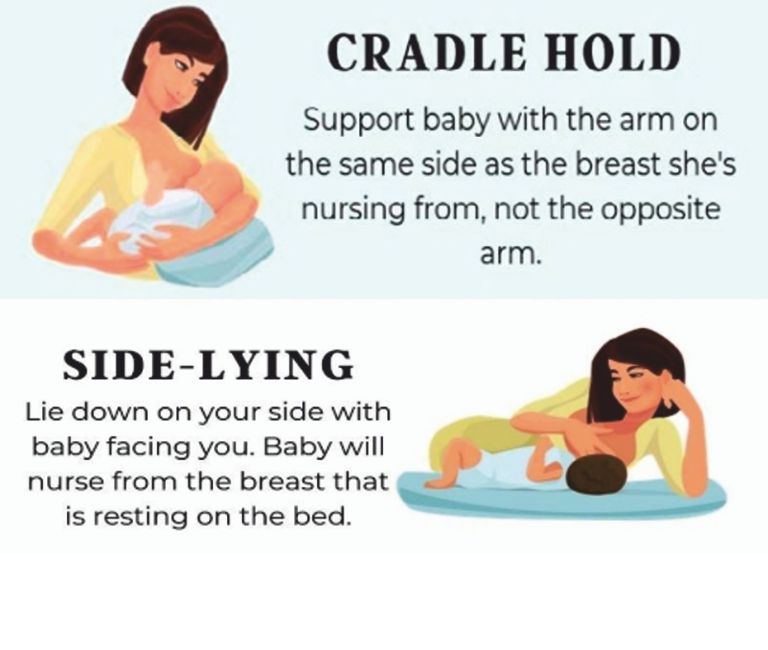
Breastfeeding
Common signs are
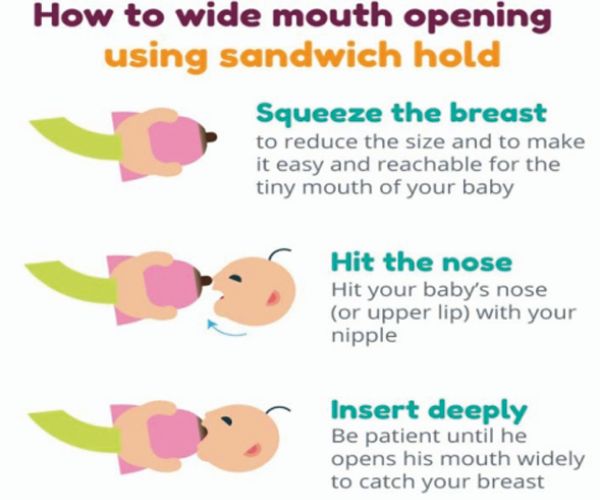
breastfeeding

breastfeeding
Good " lat ching on" i s very important and helps prevent sore nipples.
Many breastfeeding moms wonder whether their babies get enough milk for good nutrition. If your baby is getting enough breastmilk they ( baby ) should:
Breast milk provides the ideal nutrition for infants. and it’s all provided in a form more easily digested than infant formula.
It contains antibodies that help your baby fight off viruses and bacteria.
It lowers your baby’s risk of having asthma or allergies.
The physical closeness, skin-to- skin touching , and eye contact all help your baby bond with you and feel secure.
It has been linked to higher IQ scores in later childhood.
Contact your doctor if Your breasts become unusually red, swollen, hard, sore or you have an unusual discharge or bleeding from your nipples.