- A miscarriage or “spontaneous abortion”, refers to the loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks. It occurs in 15 to 20 percent of all pregnancies.
- Most miscarriages occur during the first trimester ( from first day of your last period and lasts until the end of week 12 of your pregnancy ) called early miscarriage but can also occur later on in the pregnancy, called late miscarriage.
- Different types of miscarriages can occur at different stages of your pregnancy. The symptoms and treatments will depend on the type of miscarriage.
Chemical Pregnancy
Chemical Pregnancy
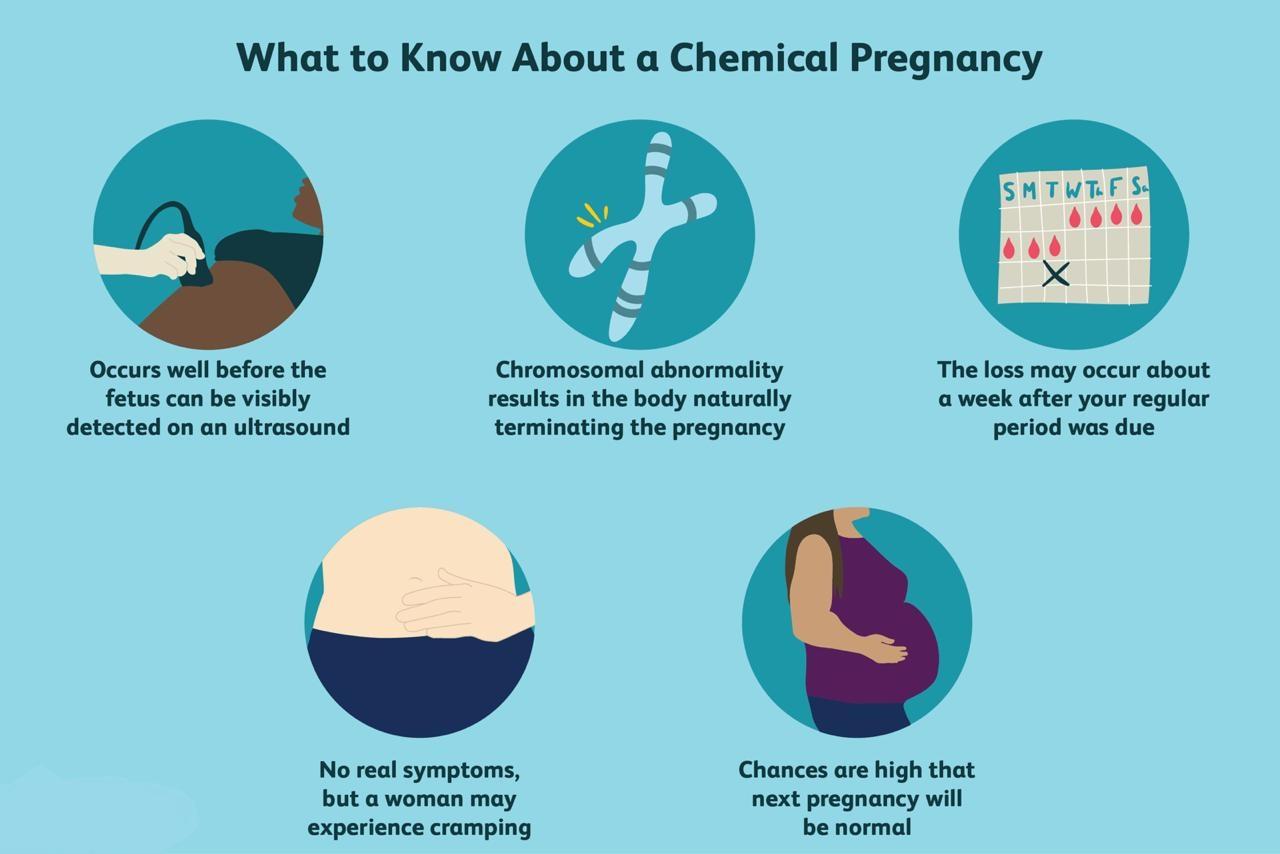
- A chemical pregnancy is a very early miscarriage.
- Which can occur before you even learn that you’re pregnant. As pregnancy tests have become more sensitive and more common, an increased number of chemical pregnancies have been diagnosed.
- Chemical pregnancy is most likely the result of chromosomal abnormalities in the fertilized egg. An egg is fertilized, but is non-viable shortly after implantation, and is never visible on ultrasound.
- There may be no signs of a chemical pregnancy. Most women simply begin to bleed around the time of their next period, though their period may arrive a few days late or be slightly heavier.
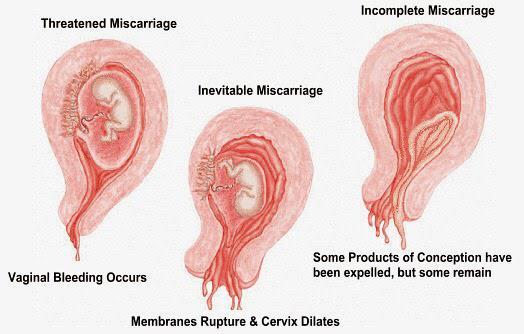
Threatened miscarriage
Types of miscarriage
- When your body is showing signs that you might miscarry, that is called a ‘threatened miscarriage’. You may have a little vaginal bleeding or lower abdominal pain. It can last days or weeks and the cervix is still closed.
- The pain and bleeding may go away and you can continue to have a healthy pregnancy and baby.
Inevitable miscarriage
- Inevitable miscarriages can come after a threatened miscarriage or without warning. There is usually a lot more vaginal bleeding and strong lower stomach cramps. During the miscarriage your cervix opens and the developing fetus will come away in the bleeding.
- There is rarely anything a doctor or you can do to protect the pregnancy except taking prescribed medicines. In the past bed rest was recommended, but there is no scientific proof that this helps at this stage.
Complete miscarriage
- A complete miscarriage has taken place when all the pregnancy tissue has left your uterus. Vaginal bleeding may continue for several days. Cramping pain much like labour or strong period pain is common – this is the uterus contracting to empty.
Incomplete miscarriage
- Sometimes, some pregnancy tissue will remain in the uterus. Vaginal bleeding and lower abdominal cramping may continue as the uterus continues trying to empty itself. This is known as an ‘incomplete miscarriage’.
- Your doctor will check with USG and decide whether or not a short procedure called a ‘Dilatation of the cervix and Curettage of the uterus’ (often known as a ‘D&C’) is necessary to remove any remaining pregnancy tissue. This is an important medical procedure done in an operation theatre.
Recurrent miscarriage
A small number of women have repeated miscarriages. If this is your third or more miscarriage in a row, it is called recurrent miscarriage or abortion.
Types of pregnancy loss
Other types of pregnancies that result in a miscarriage are outlined below.
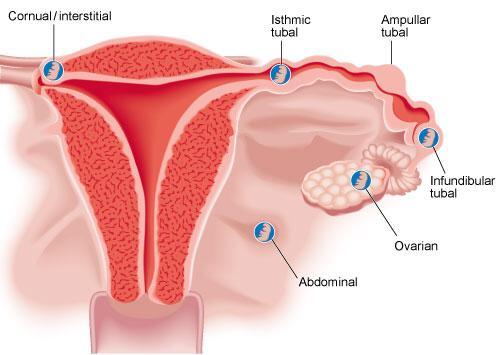
Ectopic pregnancy
- An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the embryo implants outside the uterus, usually in one of the fallopian tubes. A fetus does not usually survive in ectopic pregnancy.
- If you have an ectopic pregnancy, you may not know it at first, until it bleeds. Then you may get severe pain in your lower abdomen, vaginal bleeding, vomiting or pain in the tip of one shoulder. If you have these symptoms, it’s important to seek urgent medical attention.
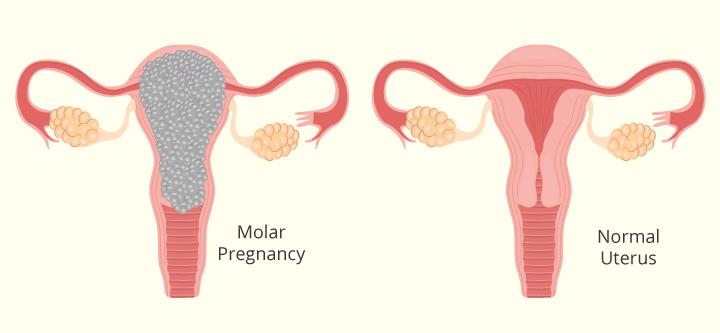
Molar pregnancy
Molar pregnancy
- A molar pregnancy is a type of pregnancy that fails to develop properly from conception. It can be either complete or partial and usually needs to be surgically removed.
Blighted ovum

Blighted ovum
- With a blighted ovum the sac develops but there is no baby inside. It is also known as an ‘anembryonic pregnancy’.
- This condition is usually discovered during a scan. In most cases, an embryo was conceived but did not develop and was reabsorbed into the uterus at a very early stage. You should meet your doctor to discuss treatment options.




